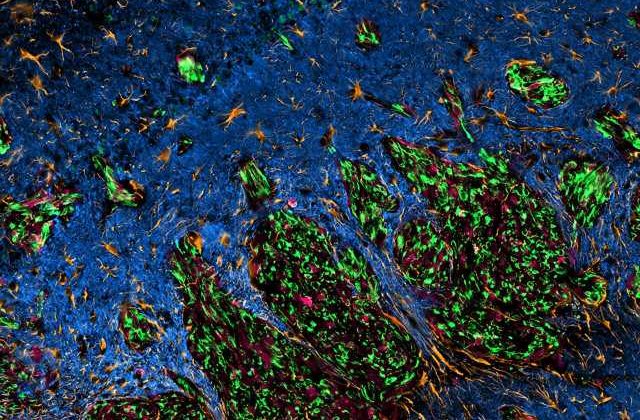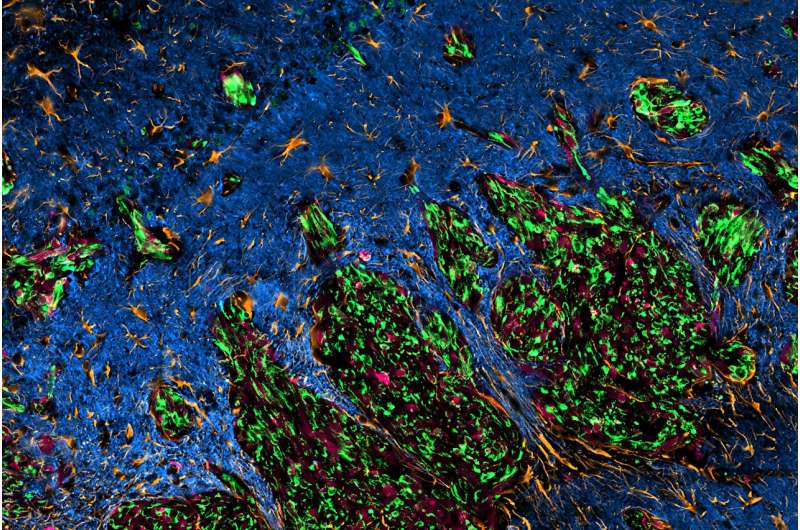
The discovery of a previously unknown molecular target has inspired what may become a therapeutic breakthrough for people with glioblastoma, the most common and aggressive brain cancer.
When people hear the word “cancer” they often picture a single mass, but glioblastoma cells are also highly invasive and spread quickly from the central mass, making it very difficult to fully eradicate. Even with current treatments such as temozolomide, the standard chemotherapy approved to treat glioblastoma, temozolomide-resistant tumors recur in more than 50% of patients with less than 1% surviving 10 years after diagnosis.
In a study published in Nature Cancer, a research team at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) showcased a new potential treatment approach for glioblastoma called a designer peptide, which targets a protein-protein interaction in the glioblastoma cells.
“By uncovering the role of a previously unknown protein-protein interaction in glioblastoma, we were able to develop a designer peptide which possesses robust therapeutic efficacy in treating all major types of glioblastoma in preclinical models,” says Dr. Xi Huang, a Senior Scientist in the Developmental & Stem Cell Biology program. “This could form the basis of next generation glioblastoma therapy.”
Protein-protein interaction holds key to glioblastoma aggression
The development of the designer peptide began when Huang and first author Dr. Weifan Dong discovered that two proteins called EAG2 and Kvβ2, both highly present in glioblastoma cells, were interacting where cancerous cells meet with healthy brain tissue.
“We examined these two proteins closely and found that when they interacted they created a potassium channel complex that is fundamental to the aggressive nature of the cancer,” says Dong, a former Ph.D. student and current post-doctoral fellow in the Huang Lab. “What’s amazing is that this EAG2-Kvβ2 potassium channel complex appears to form only in glioblastoma cells, not healthy cells.”
Excited by their findings, Huang’s team began investigating this specific interaction as a potential target for glioblastoma treatment. They determined that EAG2-Kvβ2 interaction is required for neurons to communicate with glioblastoma cells, facilitating tumor growth, invasion and chemoresistance.
The designer peptide prevents the protein-protein interaction from occurring, slowing growth and deterring the cancer from spreading into surrounding cells. In preclinical models, the designer peptide also resulted in the death of glioblastoma cells across all subtypes of glioblastoma.
“Even tumors that had developed resistance to temozolomide responded to the designer peptide,” says Dong. “But we did not observe any side effects, likely due to the EAG2-Kvβ2 interaction only seeming to be present in cancerous cells.”
Building a next-generation treatment
Over the course of the eight-year study the research team garnered important insights and support from leaders across the SickKids community, from Dr. Lu-Yang Wang, Senior Scientist in the Neurosciences & Mental Health program, to Dr. Roman Melnyk, Senior Scientist in the Molecular Medicine program and Co-Director of SPARC Drug Discovery, and Dr. Peter Dirks, Senior Scientist in the Developmental & Stem Cell Biology program.
Huang’s designer peptide discovery has been protected by the filing of a Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) application. The team plans to complete preclinical studies and advance this designer peptide into clinical trials as soon as possible.
“Our study has benefited tremendously from the vibrant research community at SickKids,” says Huang, who also holds Canada Research Chair in Cancer Biophysics. “We are continuing to work closely with other scientists and industry partners to fully unlock the potential of the designer peptide and move our research from the lab into the hands of people who need it most.”
More information:
A designer peptide against the EAG2–Kvβ2 potassium channel targets the interaction of cancer cells and neurons to treat glioblastoma, Nature Cancer (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00626-8
Journal information:
Nature Cancer
Source: Read Full Article